Who Sleep For 17 Hours A Day?
Do you ever wonder who can sleep for a staggering 17 hours a day? It sounds almost too good to be true, doesn’t it? Well, believe it or not, there are creatures on this planet that possess this incredible ability. These fascinating creatures are none other than the adorable and cuddly koalas. Yes, you heard that right! Koalas, those lovable marsupials from Australia, spend most of their lives snoozing away, catching some serious Z’s.
When it comes to sleep, koalas are the true champions. With their laid-back lifestyle, they have perfected the art of relaxation. In fact, they spend approximately 17 hours a day dozing off in the treetops. It’s like they have their own version of a never-ending slumber party! But why do koalas sleep so much? Well, it turns out that their diet of eucalyptus leaves is the culprit. These leaves are low in nutrients and require a lot of energy to digest, which leaves the koalas feeling quite lethargic. So, they compensate by sleeping for extended periods, conserving their energy for when they need it most.
So, next time you find yourself feeling envious of those who can sleep in late, just remember the koalas, the true sleep champions of the animal kingdom. While we may not be able to sleep for 17 hours a day like them, we can certainly appreciate the importance of a good nap. After all, who doesn’t love a little extra shut-eye every now and then?
There are certain animals that sleep for up to 17 hours a day. One such example is the koala. These adorable creatures spend most of their time snoozing, as their diet consists mainly of eucalyptus leaves, which provide low energy and require a lot of digestion. Other animals known for their lengthy sleep patterns include sloths and certain species of bats. These extended periods of rest allow these animals to conserve energy and survive in their respective environments.
Who Sleeps for 17 Hours a Day?
Have you ever wondered who sleeps for 17 hours a day? It may sound unbelievable, but there are actually animals that spend most of their time sleeping. In this article, we will explore some of these fascinating creatures and delve into the reasons behind their lengthy slumber.
The Sloth: A Master of Sleep
The sloth, a slow-moving mammal found in Central and South America, is notorious for its extended periods of sleep. These creatures can sleep for up to 17 hours a day, and sometimes even more! Sloths have a unique lifestyle that revolves around conserving energy, and sleep plays a crucial role in this process.
Sloths have a very low metabolic rate, which means that their bodies function at a much slower pace compared to other mammals. This slow metabolism allows them to survive on a diet that is low in nutrients, such as leaves. By sleeping for long periods, sloths are able to conserve energy and make the most of their limited food intake.
During their sleep, sloths adopt a curled-up position and can often be seen hanging upside down from tree branches. This unusual sleeping posture not only helps them blend in with their surroundings but also offers protection from predators. Sloths are known for their incredibly slow movements, and by sleeping high up in the trees, they are less likely to be detected by potential threats.
The Benefits of Extended Sleep
While sleeping for such long durations may seem excessive to us, it actually serves several important functions for animals like sloths. One of the primary benefits of extended sleep is the conservation of energy. By sleeping for extended periods, sloths are able to maintain their low metabolic rate and survive on their specialized diet.
Another benefit of prolonged sleep is the regeneration and repair of tissues. During sleep, the body goes into a state of rest and recovery, allowing cells to repair any damage and promoting overall healing. For slow-moving creatures like sloths, who often encounter physical challenges in their environment, this extended sleep is essential for their well-being.
Furthermore, extended sleep also plays a role in the preservation of water. Sloths have a limited ability to retain water, and by sleeping for long durations, they reduce the amount of water they lose through activities such as sweating and urination. This adaptation helps them survive in their humid rainforest habitats, where water sources can be scarce.
In conclusion, the sloth is a remarkable creature that sleeps for up to 17 hours a day. This extended sleep is not only a result of their low metabolic rate but also serves several important functions. By conserving energy, promoting tissue repair, and preserving water, sloths are able to thrive in their unique and challenging environments.
The Koala: A Sleepy Eucalyptus Lover
Another animal known for its lengthy sleep sessions is the koala. These adorable marsupials, native to Australia, spend an average of 18 to 22 hours a day sleeping! While this may seem like an excessive amount of sleep, it is essential for their survival and well-being.
Koalas have a specialized diet consisting mainly of eucalyptus leaves. However, these leaves are low in nutrients and require a lot of energy to digest. To compensate for this, koalas conserve energy by sleeping for long periods. This extended sleep allows their bodies to focus on digestion and the processing of the tough and fibrous eucalyptus leaves.
Like sloths, koalas are also known for their slow metabolism. This means that their bodies operate at a slower pace, requiring less energy and allowing them to survive on their nutrient-deficient diet. By spending most of their time sleeping, koalas are able to maximize their energy conservation and make the most of their limited food intake.
The Importance of Sleep for Koalas
The extended sleep of koalas serves several important purposes. One of the primary reasons they sleep for such long durations is to aid in digestion. Eucalyptus leaves are tough and fibrous, and koalas need to spend a significant amount of time breaking down these leaves in their digestive system. By sleeping, they allow their bodies to focus on this essential process.
Sleep also plays a crucial role in the conservation of water for koalas. Like sloths, koalas have a limited ability to retain water, and by sleeping, they reduce the amount of water they lose through activities such as sweating and urination. This adaptation is particularly important for koalas, as they inhabit regions of Australia where water sources can be scarce.
Furthermore, sleep is essential for the overall well-being of koalas. During sleep, their bodies undergo important physiological processes, such as tissue repair and hormone regulation. These processes help koalas maintain their health and vitality, enabling them to thrive in their unique eucalyptus forest habitats.
In summary, koalas are fascinating creatures that sleep for extended periods to conserve energy, aid digestion, and preserve water. Their slow metabolism, combined with their specialized diet, makes sleep a vital aspect of their survival. By spending most of their time sleeping, koalas have adapted to thrive in the challenging conditions of their eucalyptus forest homes.
Other Animals with Lengthy Sleep Habits
Apart from sloths and koalas, there are several other animals that exhibit lengthy sleep habits. Let’s explore some of these creatures and discover the reasons behind their prolonged slumber.
The Brown Bat: Sleepy Nocturnal Flyers
Brown bats, also known as little brown bats, are nocturnal mammals that are famous for their exceptional sleeping abilities. These small creatures can sleep for up to 19 hours a day, making them some of the sleepiest animals in the world.
Bats have a unique sleeping pattern called torpor, which is similar to hibernation. During torpor, bats lower their body temperature, slow down their metabolism, and enter a state of deep sleep. This adaptation allows them to conserve energy and survive periods of food scarcity, especially during the winter months.
Torpor also helps bats cope with their high-energy lifestyle. Despite their small size, bats are highly active animals that engage in activities such as flying, hunting for insects, and mating. By sleeping for extended periods, bats can recharge their energy reserves and maintain their physical performance.
The Fascinating World of Bat Sleep
Bats’ sleep patterns are closely tied to their unique feeding habits. As nocturnal creatures, bats rely on echolocation to navigate and locate their prey. Echolocation is a complex process that requires a lot of energy, and by sleeping for long durations, bats are able to replenish the energy they expend during their nightly hunting missions.
Another interesting aspect of bat sleep is their ability to sleep while hanging upside down. Bats have specially adapted tendons and muscles in their feet that allow them to grip onto surfaces, such as tree branches or cave walls, without using any energy. This hanging sleep position allows bats to conserve energy and be ready for flight at a moment’s notice.
In conclusion, brown bats are remarkable creatures that sleep for up to 19 hours a day. Their unique sleeping pattern of torpor helps them conserve energy, cope with their high-energy lifestyle, and replenish the energy expended during echolocation. The world of bat sleep is a fascinating one, showcasing the incredible adaptations these creatures have developed.
The Lion: King of the Sleep Jungle
While we often associate lions with their majestic presence and powerful roars, these big cats are also known for their extensive sleep habits. Lions can sleep for up to 20 hours a day, making them one of the sleepiest animals in the animal kingdom.
The lifestyle of lions revolves around hunting and conserving energy. By sleeping for long durations, lions are able to conserve their energy for hunting and other essential activities. This extended sleep also helps them cope with the heat of their African savannah habitat, as they are most active during the cooler hours of the day.
Lions are social animals that live in prides, which consist of several females and their cubs, along with a few male lions. Sleeping for extended periods also allows lions to synchronize their activities within the pride. By sleeping together, they can coordinate their hunting and ensure the safety and well-being of the group.
The Role of Sleep in Lion Survival
Sleep plays a crucial role in the survival of lions. During sleep, lions undergo important physiological processes, such as muscle repair and hormone regulation. These processes help maintain their strength and overall health, enabling them to thrive in their challenging and competitive environment.
Sleep also aids in the digestion of their large meals. Lions are apex predators that primarily feed on large herbivores, such as zebras and wildebeests. These meals can be quite substantial and require a significant amount of energy to digest. By sleeping, lions allow their bodies to focus on the digestion process, ensuring efficient nutrient absorption.
Furthermore, sleep helps lions regulate their body temperature. The African savannah can be scorching hot during the day, and by sleeping for extended periods, lions can conserve energy and avoid overheating. This adaptation is especially important for hunting, as they are most active during the cooler hours of the day.
In summary, lions are magnificent animals that sleep for up to 20 hours a day. Their extended sleep is essential for energy conservation, digestion, synchronization within the pride, and overall survival. The sleep habits of lions highlight the importance of rest and recovery in the animal kingdom.
Other Animals with Unique Sleep Patterns
In addition to sloths, koalas, bats, and lions, there are numerous other animals with intriguing sleep patterns. Let’s explore a few more fascinating creatures and their sleep habits.
The Armadillo: The Sleepy Armor-Wearer
Armadillos, with their armored shells and fascinating digging abilities, are known for their unique sleep patterns. These nocturnal mammals sleep for around 16 hours a day, spending most of their waking hours searching for food and navigating their surroundings.
Armadillos have a low metabolic rate, which allows them to conserve energy during their extended sleep periods. This adaptation is particularly important for these insectivorous creatures, as their diet consists mainly of insects and other invertebrates. By sleeping for long durations, armadillos can minimize their energy expenditure and maximize their chances of finding food.
Another interesting aspect of armadillo sleep is their ability to enter a state of torpor. Similar to bats, armadillos can lower their body temperature and slow down their metabolic rate during periods of inactivity. This physiological adaptation helps them cope with extreme weather conditions and food scarcity.
The Python: A Serpentine Slumberer
Pythons, the large constrictor snakes found in various parts of the world, are known for their impressive sleep habits. These reptiles can sleep for up to 18 hours a day, often in a coiled position to conserve body heat.
Pythons are ambush predators that rely on their ability to strike and constrict their prey. By sleeping for extended periods, pythons conserve energy and wait for the perfect opportunity to capture their next meal. This sleep pattern also helps them regulate their body temperature, as they are ectothermic and rely on external sources of heat.
During sleep, pythons enter a state of rest and recovery, allowing them to digest their large meals. After a successful hunt, pythons can consume prey that is much larger than their own body size. This requires a significant amount of energy for digestion, and sleeping helps facilitate this process.
The Elephant: Slumbering Giants
Elephants, the largest land animals on Earth, have their own unique sleep patterns. These majestic creatures sleep for around 4 to 6 hours a day, often in short bursts of 30 minutes to 2 hours at a time. Their sleep is typically divided into several periods throughout the day and night.
Due to their massive size and herbivorous diet, elephants require a substantial amount of food and water. By sleeping for shorter durations, elephants can spend more time feeding and meeting their nutritional needs. This sleep pattern also helps them remain vigilant against potential threats in their surroundings.
Elephants are highly social animals that live in close-knit family groups called herds. Sleeping in shorter bursts allows them to stay connected and coordinate their activities within the herd. It also ensures that there is always someone on guard to watch over the rest of the group.
The Fascinating World of Animal Sleep
The world of animal sleep is a diverse and fascinating one. From sloths and koalas to bats and lions, each species has its own unique sleep patterns and adaptations. Sleep serves a variety of functions for these animals, including energy conservation, digestion, tissue repair, and synchronization within social groups.
By understanding the sleep habits of different animals, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable adaptations and strategies that have evolved over time. Whether it’s the slow and steady sleep of a sloth or the brief rest periods of an elephant, each sleep pattern plays a vital role in the survival and well-being of these incredible creatures.
As we continue to explore the world of animal sleep, we uncover new insights into the intricate balance between rest and activity, and the importance of sleep in maintaining a healthy and thriving ecosystem. So, the next time you find yourself wondering who sleeps for 17 hours a day, remember that the animal kingdom is full of captivating sleepers, each with their own unique story to tell.
Who Sleeps for 17 Hours a Day?
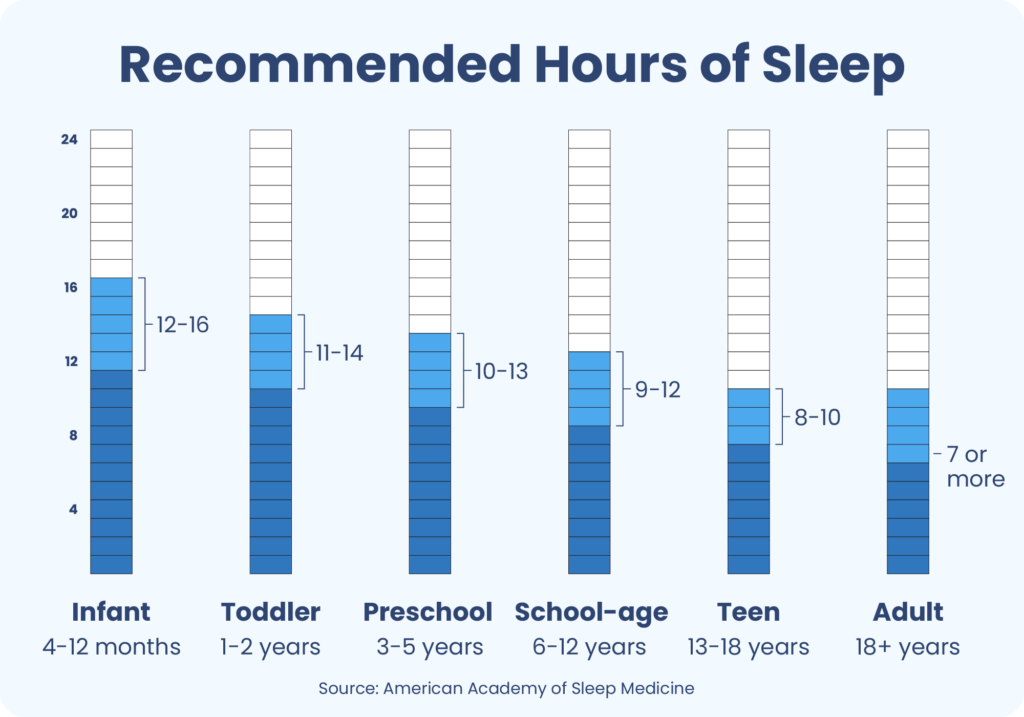
- 1. Some newborn babies sleep for about 17 hours a day.
- 2. Koalas are known to sleep for up to 17 hours a day.
- 3. Sloths are famous for their long sleeping hours, which can reach up to 17 hours a day.
- 4. Cats, especially kittens, can sleep for around 17 hours a day.
- 5. Certain species of bats also sleep for approximately 17 hours a day.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do some animals sleep for 17 hours a day?
Sleep patterns vary among different animal species. Some animals, like certain mammals, reptiles, and birds, sleep for extended periods of time due to their unique physiological and behavioral adaptations. These animals require more sleep to fulfill their specific needs, such as conserving energy, digesting food, or avoiding predators.
For example, sloths are known to sleep for up to 17 hours a day because their diet consists mainly of low-energy foods, like leaves, which take longer to digest. By sleeping for extended periods, sloths can conserve energy and maintain their low metabolic rate, allowing them to survive in their natural habitat.
Which animals sleep for 17 hours a day?
Several animal species are known to sleep for approximately 17 hours a day. Some examples include:
- Sloths
- Opossums
- Koalas
- Giant pandas
- Some bats
These animals have specific physiological and ecological adaptations that require them to sleep for long durations.
It’s important to note that while these animals sleep for extended periods, their sleep patterns may vary based on factors such as age, reproductive cycles, and environmental conditions.
What are the benefits of sleeping for 17 hours a day?
Sleeping for 17 hours a day can provide various benefits for animals that have adapted to this sleep pattern. Some of the benefits include:
Energy conservation: Sleeping for extended periods helps animals conserve energy, especially if they have a low-energy diet or are adapted to a sedentary lifestyle.
Metabolic regulation: Longer sleep durations allow animals to regulate their metabolism and maintain optimal physiological functions.
Protection from predators: Some animals, like sloths, sleep for extended periods to avoid predation. By minimizing their movement and staying hidden in trees, they can reduce the risk of being detected by predators.
Brain development: Sleep plays a crucial role in brain development and memory consolidation. Animals that sleep for 17 hours a day may benefit from enhanced cognitive functions and improved learning abilities.
Do humans ever sleep for 17 hours a day?
While it is uncommon for humans to sleep for 17 hours a day, certain circumstances or medical conditions can lead to excessive sleep durations. Examples include:
Infants: Newborn babies can sleep for up to 17 hours a day due to their rapid growth and development.
Medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as certain sleep disorders or neurological disorders, can cause individuals to experience prolonged sleep durations.
Extreme fatigue or sleep deprivation recovery: In rare cases of extreme fatigue or sleep deprivation, individuals may sleep for extended periods as their body tries to recover and restore energy levels.
What are the risks of sleeping for 17 hours a day?
While sleeping for 17 hours a day may be normal for certain animals, it can be a cause for concern in humans. Excessive sleep durations in humans can be a symptom of underlying health issues, such as:
Depression or mental health disorders: Sleeping excessively can be a sign of depression or other mental health disorders. It is essential to seek professional help if excessive sleep becomes a persistent pattern.
Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as sleep apnea or thyroid disorders, can disrupt sleep patterns and cause excessive sleep durations. These conditions should be evaluated and treated by a medical professional.
Medication side effects: Some medications, including certain antidepressants or sedatives, can cause drowsiness and prolonged sleep. Discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider if you suspect medication may be causing excessive sleep.
If you find yourself consistently sleeping for extended periods or experiencing excessive sleepiness, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
The Danger of Sleeping Too Much
Final Thoughts
And there you have it, folks! The fascinating world of creatures that sleep for 17 hours a day. Who would have thought that such prolonged slumber could exist? But it turns out that there are indeed animals out there who enjoy their beauty rest to the max. From the adorable koalas to the mysterious sloths, these creatures have mastered the art of relaxation.
But let’s not forget that while they may seem lazy to us, their long sleep durations serve important purposes. It’s all about survival and energy conservation. They have adapted to their environments in unique ways, allowing them to thrive despite their seemingly excessive sleep habits. And who can blame them? After all, getting a good night’s sleep (or day’s sleep, in their case) is crucial for rejuvenation and overall well-being.
So, the next time you find yourself in need of some extra shut-eye, just remember that you’re not alone. There are creatures out there who take sleep to a whole new level. Embrace the power of slumber and appreciate the wonders of nature’s sleep champions. And who knows, maybe we can all learn a thing or two from these sleep experts when it comes to getting the rest we need. Sweet dreams, everyone!